MAESTRO: Adaptive Sparse Attention and Robust Learning for Multimodal Dynamic Time Series
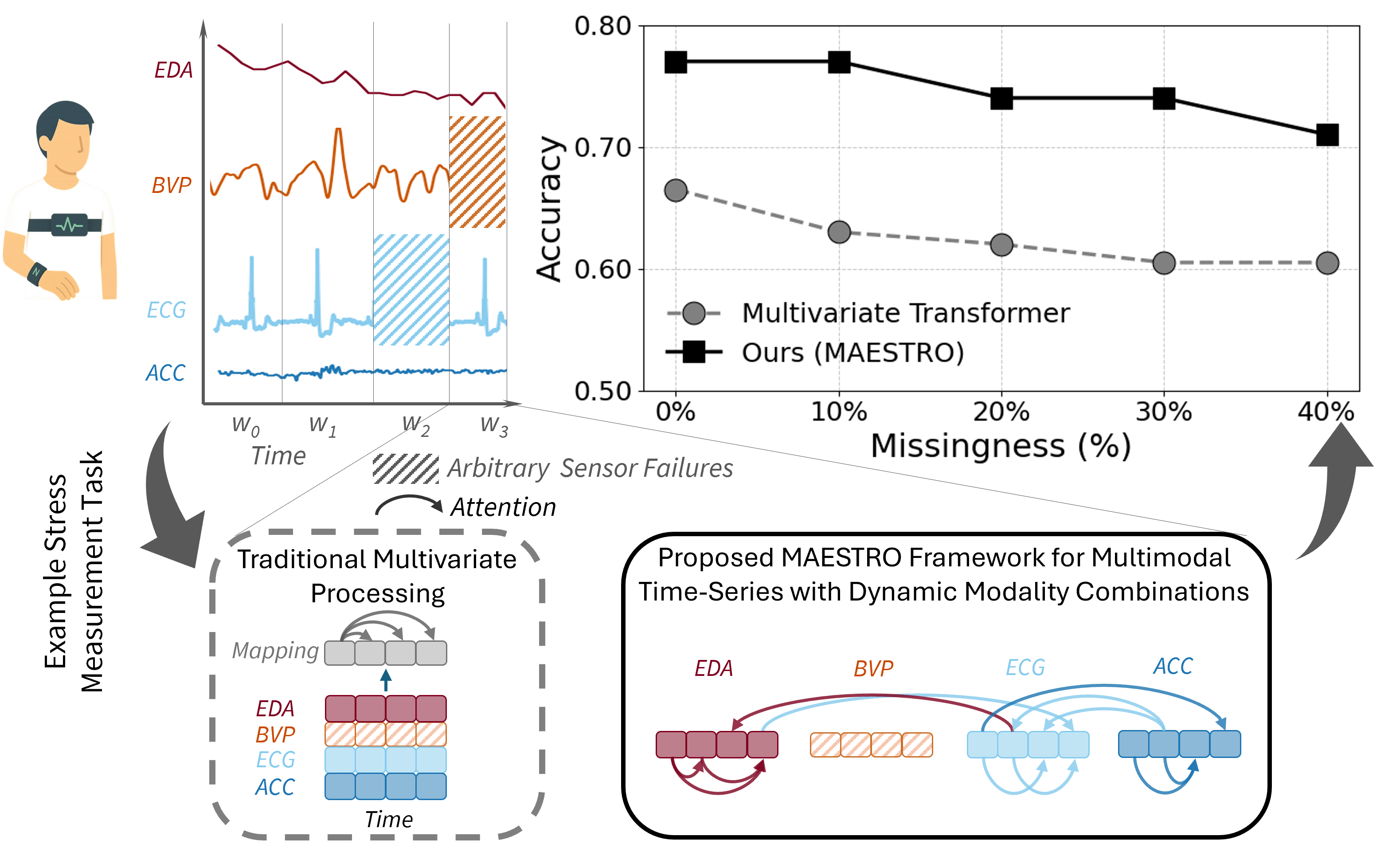
Real-world multimodal time series (wearables, mobile sensing, clinical monitoring) rarely comes with all modalities present. Sensors can be missing, corrupted, or intermittently unavailable, leading to arbitrary missingness patterns that break many multimodal models. MAESTRO addresses this by combining missingness-aware symbolic modeling with adaptive sparse attention and sparse MoE routing, achieving strong accuracy while keeping computation practical.
Why MAESTRO works well in practice
- Robust to missing modalities (arbitrary combinations, not a single fixed pattern).
- Adaptive compute allocation across modalities (learned attention budgeting).
- Efficient via sparse attention and sparse MoE (top-k routing).
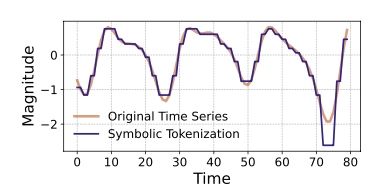
- Symbolic tokenization reduces sensitivity to noise and sampling irregularities.
Core Idea: Missingness-Aware Symbolic Modeling
MAESTRO uses symbolic tokenization (SAX-style) to convert each modality’s time-series segments into discrete tokens. Crucially, it reserves an explicit missing token to represent absent segments, allowing the model to learn the meaning of missingness instead of relying on heuristic masking or zero-filling.
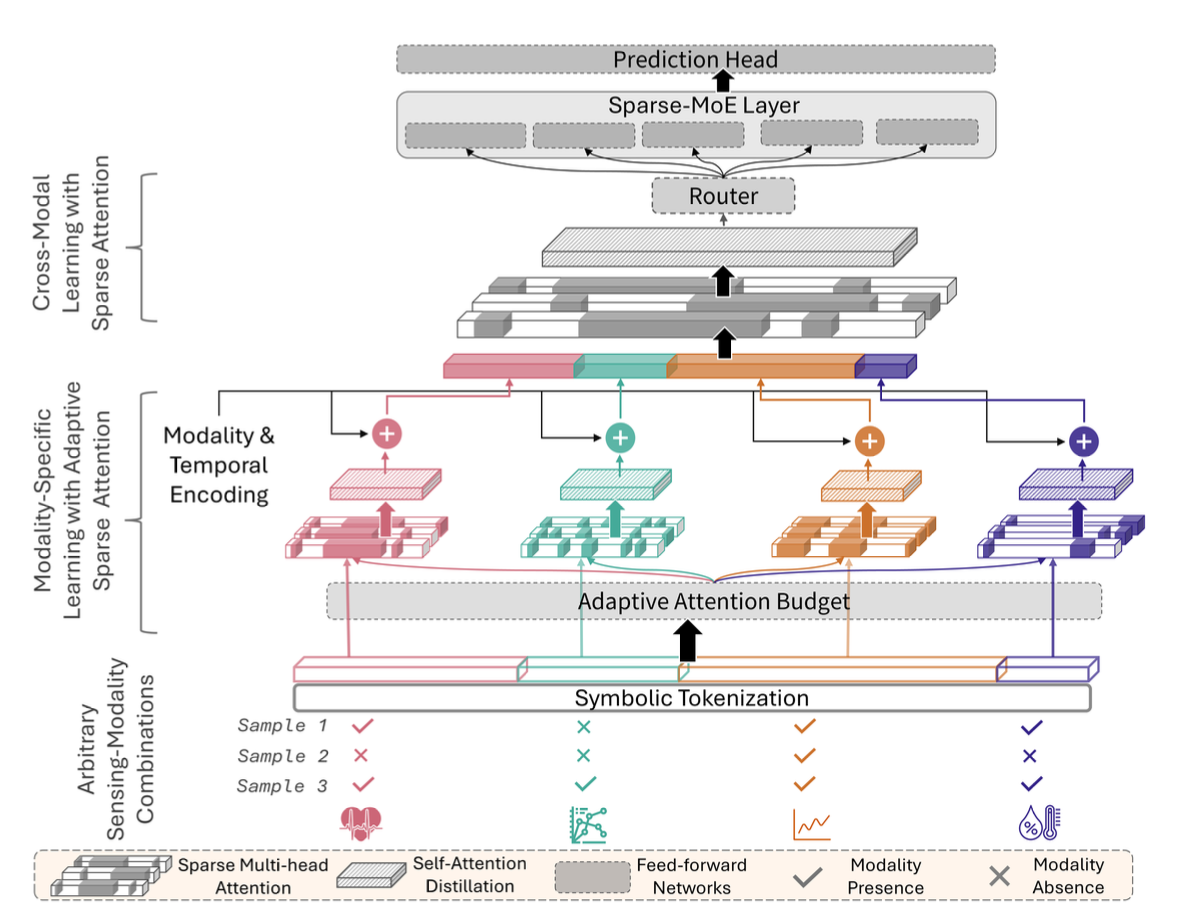
Architecture
MAESTRO has three key components:
1) Adaptive sparse intra-modal modeling
Each modality is encoded with sparse attention, with a learned budget controlling how much attention capacity each modality receives (based on modality availability and utility).
2) Sparse cross-modal attention
Encoded modality streams are fused using sparse cross-modal attention to capture inter-modal dependencies efficiently.
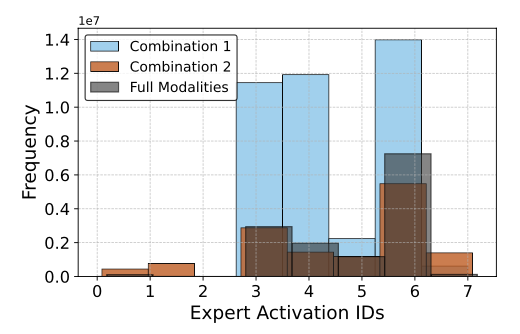
3) Sparse MoE routing (specialization)
A sparse MoE module routes tokens to experts (top-k), enabling specialization for different modality-availability patterns.
Key Results
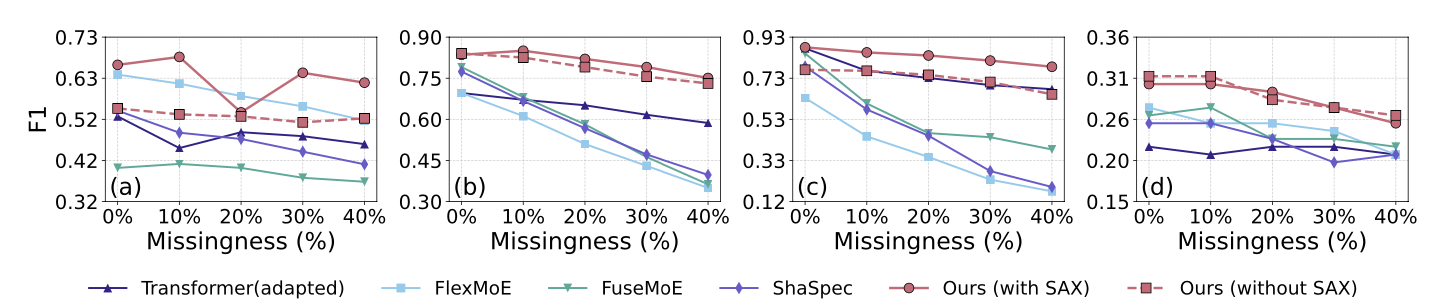
Missing-modality robustness (paper-reported highlights)
- Under 40% missingness, MAESTRO outperforms the best missingness-resilient multimodal baseline by an average relative Macro-F1 gain of 59%.
- Compared to a modality-dropout-adapted Transformer, MAESTRO improves performance by 25% relatively.
- The explicit symbolic missing token yields an average relative gain of 11%.
- Across datasets, MAESTRO improves over the best baseline by 7.6% absolute under 10% missingness, and 9.4% absolute under 40% missingness.
Full-modality performance snapshot (Acc / Macro-F1)
With symbolic tokenization enabled (Table 2), MAESTRO achieves:
- WESAD: Acc 0.77 ± 0.02 / F1 0.66 ± 0.01
- DaliaHAR: Acc 0.83 ± 0.01 / F1 0.84 ± 0.01
- DSADS: Acc 0.88 ± 0.01 / F1 0.88 ± 0.01
- MIMIC-III: Acc 0.78 ± 0.01 / F1 0.30 ± 0.01
Efficiency snapshot (WESAD setting)
On WESAD (Table 3), MAESTRO delivers strong accuracy with practical compute:
- MAESTRO: Acc 0.77 ± 0.04, 3066 MMAC, 6.13 GFLOPs, 1.39M params
- For reference: MULT uses 26.65 GFLOPs and 3.71M params (much heavier), while MAESTRO stays far more efficient.
Code and Media
Publications
-
MAESTRO: Adaptive Sparse Attention and Robust Learning for Multimodal Dynamic Time Series.
NeurIPS 2025.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25278